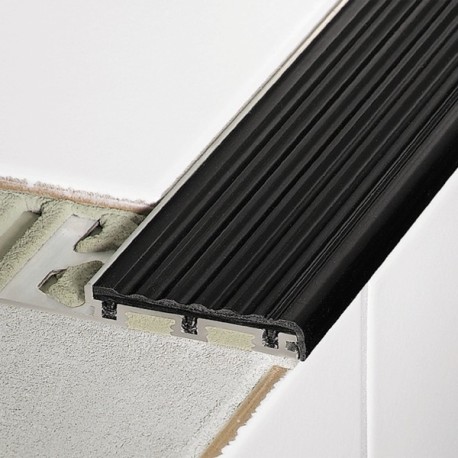
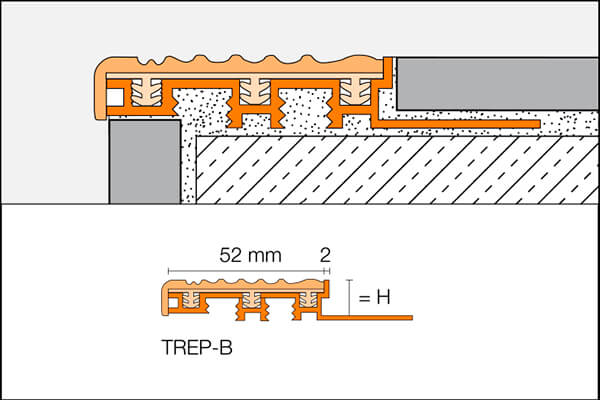
The stair edging profile for tiles Schlüter TREP-B are special profiles for creating slip resistant and visually attractive stair nosings. They are suitable for use in areas subjected to heavy foot-traffic, such as offices or public buildings. TREP-B feature a tread surface that can be replaced in case of damage or wear.
Stair edge profile that protects the step’s front edge while its special slip resistant tread is designed to increase visual awareness, adding a high degree of safety to stairs.
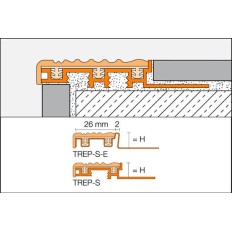
All three profile types have been approved for use in applications where the risk of slipping exists (BIA test certificate, slip resistance assessment group R 9). Matching end caps are available as accessories.
This stair profile TREP-TAP provides additional coverage for front edges to comply with disability requirements (DDA) in public buildings.

Material
TREP-B have aluminium support sections. All three profile types include a tread insert consisting of a rigid PVC base section and soft PVC slip resistant surface. The width of the Schlüter TREP-B tread surface is 52 mm. The support section includes a trapezoid perforated anchoring leg for securing the profile in the tile adhesive.
Material properties and areas of application
In special cases, the suitability of a proposed type of profile must be verified, based on the anticipated chemical, mechanical and/ or other stresses. Schlüter TREP-SE, with a support section made of stainless steel, is particularly well suited for areas of application where resistance to chemicals and acids is necessary and where alkaline exposure is anticipated, e.g. through the reaction of water with cementitious materials.
The stair edge profile Schlüter TREP- B, with aluminium support sections, are resistant to chemical stresses commonly encountered in tiled coverings on stairs. Cementitious materials, in conjunction with moisture, become alkaline. Since aluminium is sensitive to alkaline substances, exposure to the alkali (depending on the concentration and time of exposure) may result in corrosion. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the profile is solidly embedded in the setting material and that all cavities are filled to prevent the collection of alkaline water.
Installation
- Select the stair nosing profile according to the tile thickness.
- Align the covering material at the riser.
- Apply a suitable tile adhesive to the edge area above the step riser.
- Fill the hollow spaces on the underside of the profile with suitable tile adhesive. Note for steps 3 and 4: In case of thicker adhesive layers in the edge area, it may be necessary to add sand to the dry-setting thin bed adhesive in accordance with manufacturer instructions or to use a medium bed mortar.
- Embed the stair edge trim fully into the adhesive bed and align the profile in such a way that the front edge of the support profile is flush with the riser tile.
- Trowel additional setting material over the trapezoid perforated anchoring leg and the tread of the stair step to ensure full coverage.
- Solidly embed the horizontal tiles and align them flush with the top edge of the profile. Full coverage must be obtained between the tile and the profile’s anchoring leg.
- Leave a gap of approx. 2 mm between the tile and the profile.
- Completely fill the space between the tile and the profile with grout.
- The front edge cover profile Schlüter TREP-TAP can only be used in conjunction with TREP-S and -B, which have aluminium support profiles. The profile is either inserted laterally through the designated groove or snapped into place from below. Attach the back of TREP-TAP to the riser (e.g. with Schlüter-KERDI-FIX).
Maintenance
The stair edging profiles requires no special or preventative maintenance. The tread insert can be replaced in case of damage or wear.
Stainless steel surfaces exposed to the environment or aggressive substances should be cleaned periodically using a mild household cleaner. Regular cleaning maintains the neat appearance of stainless steel and reduces the risk of corrosion. All cleaning agents must be free of hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acid.
Avoid contact with other metals such as steel, since this can cause rust. This also includes tools such as trowels or steel wool, i.e. tools used to remove mortar residue.